9 Neuromarketing Concepts Every Marketer Should Master in 2025


9 Neuromarketing Concepts Every Marketer Should Master in 2025
People don’t buy logically. They buy emotionally — and then justify their choices with logic.
That’s exactly why some ads make you cry, why subscription pricing feels “lighter” when shown per day, and why you almost never pick the cheapest Netflix plan.
Welcome to neuromarketing — the science of applying psychology and neuroscience to understand how people make buying decisions.
If you’re still marketing by throwing features at customers and hoping they’ll convert, it’s time to level up. Here are 9 neuromarketing concepts that will transform your marketing game in 2025.
1. The Framing Effect
🔹 What it is: The way you phrase something completely changes how people perceive it.
95% fat-free” feels healthier than “contains 5% fat”.
Save ₹1,000” feels more exciting than “Spend ₹9,000”.
Application: Use positive framing in product descriptions, ads, and offers to create instant appeal.
2. The Affordability Illusion
🔹 What it is: Breaking down a price into smaller chunks makes it feel more affordable.
₹600/month vs. “Just ₹20/day.”
Annual subscription vs. “Only ₹49/week.”
Application: SaaS brands, subscription services, gyms, and even e-commerce can use this to reduce purchase hesitation.
3. The Rule of 3
🔹 What it is: When given three options, people rarely choose the cheapest. They usually go for the middle option.
Netflix: Basic, Standard, Premium.
Coffee shops: Small, Medium, Large (and most people go Medium).
Application: Create three-tier pricing to nudge customers toward the package you actually want them to buy.
4. The IKEA Effect
🔹 What it is: People value things more when they’ve put effort into creating them.
You’ll never throw away that IKEA shelf you built, even if it’s wobbly.
Custom pizza builder? Customers love it more because they “made” it.
Application: Give customers a sense of involvement — customisation, DIY options, polls, or community-driven ideas.
5. The Power of Free
🔹 What it is: People overvalue free things, even if they don’t need them.
Buy 1, Get 1 Free” feels more tempting than “50% off.”
Free shipping often drives more sales than a bigger discount.
Application: Add “free” strategically — free trial, free gift, free guide — to trigger faster conversions.
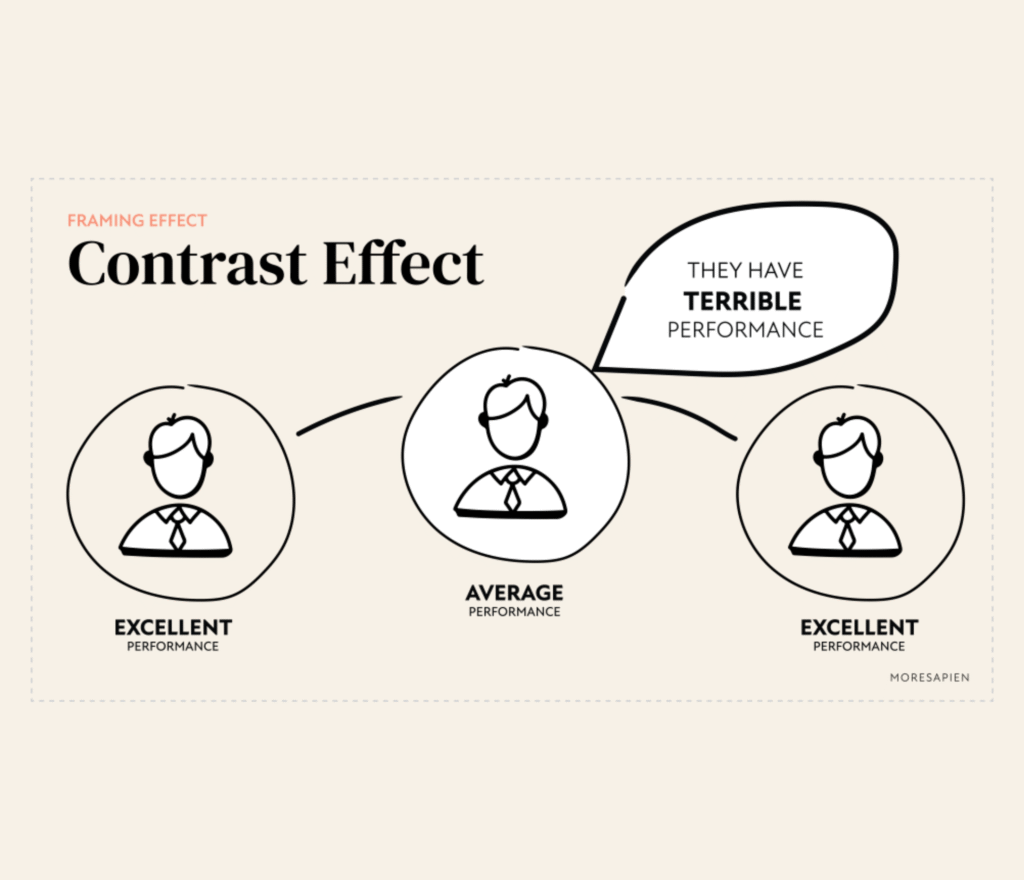
6. The Contrast Effect
🔹 What it is: People evaluate something by comparing it to what’s next to it.
₹8,000 shoes feel expensive until you see them next to a ₹20,000 pair.
A ₹999 plan looks better after a ₹1,999 plan.
Application: Always position your “hero offer” next to a higher-priced anchor to boost perceived value.
7. The Paradox of Choice
🔹 What it is: Too many choices = decision paralysis. Customers freeze and buy nothing.
Think about scrolling Netflix for 20 minutes and watching nothing.
Too many menu options at a restaurant overwhelm you.
Application: Simplify. Curate fewer, clearer options so the decision feels easier and faster.
8. Anchoring Bias
🔹 What it is: The first number people see influences how they judge later prices.
A ₹5,000 bag looks cheap after showing a ₹15,000 one.
Was ₹2,999, Now ₹1,499” feels like a steal.
Application: Always anchor with a higher price first before showing your real offer.

9. The Endowment Effect
🔹 What it is: People value things more once they feel ownership.
Free 7-day trials work because people feel like it’s already theirs.
Adding products to a cart increases attachment even before checkout.
Application: Offer free trials, samples, or interactive product demos to build ownership before purchase.
Final Thoughts
Great marketing doesn’t just list features. It taps into human psychology to make buying feel like the natural choice.
By understanding neuromarketing, you’re not manipulating customers — you’re making it easier for them to say yes to something they already want.
And when done right? Neuromarketing becomes your strongest growth engine.
Want to build campaigns that blend creativity with consumer psychology?
At Digitally Desi, we help brands craft strategies that convert.
Check us out here: digitallydesi_media